1. ConX Neural Networks¶
1.1. The On-Ramp to Deep Learning¶
Built in Python 3 on Keras 2.
Binder
CircleCI
codecov
Documentation Status
PyPI version

Read the documentation at conx.readthedocs.io
Ask questions on the mailing list: conx-users
Implements Deep Learning neural network algorithms using a simple interface with easy visualizations and useful analytics. Built on top of Keras, which can use either TensorFlow, Theano, or CNTK.
A network can be specified to the constructor by providing sizes. For example, Network(“XOR”, 2, 5, 1) specifies a network named “XOR” with a 2-node input layer, 5-unit hidden layer, and a 1-unit output layer. However, any complex network can be constructed using the net.connect() method.
Computing XOR via a target function:
import conx as cx
dataset = [[[0, 0], [0]],
[[0, 1], [1]],
[[1, 0], [1]],
[[1, 1], [0]]]
net = cx.Network("XOR", 2, 5, 1, activation="sigmoid")
net.dataset.load(dataset)
net.compile(error='mean_squared_error',
optimizer="sgd", lr=0.3, momentum=0.9)
net.train(2000, report_rate=10, accuracy=1.0)
net.test(show=True)
Creates dynamic, rendered visualizations like this:
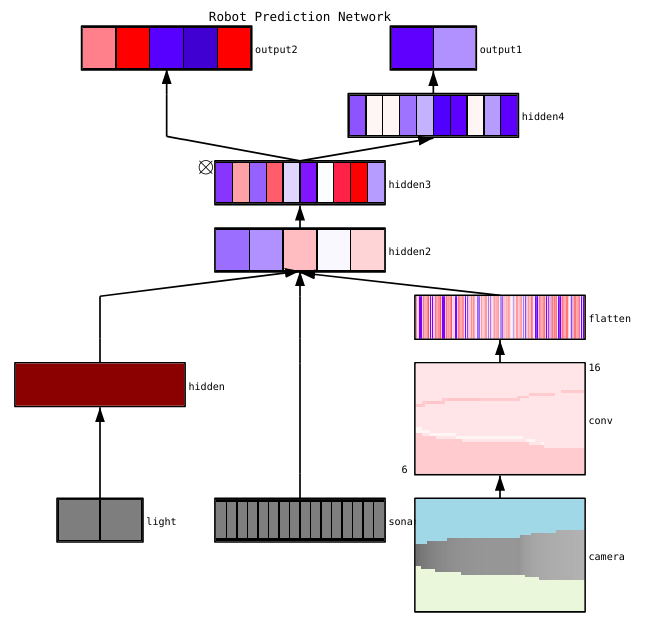
1.2. Examples¶
See conx-notebooks and the documentation for additional examples.
1.3. Installation¶
See How To Run Conx to see options on running virtual machines, in the cloud, and personal installation.